Digital marketing is a complex field that utilizes specific jargon to describe different practices. For example , SEO (search engine optimization) and PPC (pay per click) are both forms of online advertising; web design refers broadly speaking for any project involving computer-based work such as creating websites or software applications.
The most common terms you’ll come across when working in this industry often have more than one meaning depending on the context they’re being used within – which can make them hard enough already without adding in some unfamiliar language too! That’s why we’ve put together this ultimate digital marketing glossary.
#
301 Redirect – A method of redirecting a visitor from one web page to another web page. This type of redirect is to be used for permanent redirects (example: you own websiteA.com and websiteB.com but you only want one website. You would 301 redirect all of the traffic from websiteB.com to websiteA.com so that all visitors end up on websiteA.com)
302 Redirect – A method of redirecting a visitor from one page to another web page, used for temporary situations only. For permanent redirects, instead use a 301.
404 Error – The error message that appears when a visitor tries to go to a web page that does not exist.
A
A/B testing – A common method of advertising. It involves creating two versions (ex: ad copy, an email or image) that will be tested against each other in order to see which performs better; when doing the experiment it’s important not make any changes from version A-to -version B so we know what our audience prefers!
Ad Extensions – Additional pieces of information that can be added to Google Adwords ads, including reviews, address, pricing, callouts, app downloads, sitelinks, and click-to-call. Ad extensions help advertisers create richer, more informative ads that take up more on-page real estate, which generally lead to higher Click Through Rates.
Ad Manager Account – An advertising account on Facebook that allows you to run ads on the Facebook Ad Network.
Ad fatigue – This is what happens when users are over-exposed to the same ad and it results in less clicks and conversions. Commonly used in Facebook, advertisers will use this as a benchmark to determine when to update ad creative so they stay relevant and give users a positive advertising experience.
Ad Network – A grouping of websites or digital properties (like apps) where ads can appear. For example, Google has 2 ad networks: the search network (text ads that appear in search results) and the display network (image ads that appear on millions of websites that have partnered with Google).
Adwords (Google Adwords) – A Google owned program that is used by advertisers to place ads on Google search results pages, on Youtube, and on Google ad network sites. Adwords is the primary platform for PPC advertising.

Algorithm – In digital marketing, this is a complex set of rules search engines and advertising platforms use to choose which ads a user sees first. This is normally made up of keyword bidding, ad relevance, quality score from the landing page, optimization on the website, and other various factors.
Alt Text (or Alternative Text) – An attribute added to HTML code for images, used to provide vision impaired website visitors with information about the contents of a picture. Best practice dictates that all images on a website should have alt text, and that the text should be descriptive of the image.
Analytics (or Google Analytics) – A Google platform that allows webmasters to collect statistics and data about website visitors. Google Analytics (sometimes abbreviated as GA) allows webmasters to see where web traffic comes from and how visitors behave once on the site.
Anchor Text – The clickable words in a hyperlink. In SEO, anchor text is a ranking signal to Google, as it provides context about the destination site. For example, if many websites link to one particular website using the anchor text “free stock photos”, Google uses that information to understand the destination site is likely a resource with free stock photos. Theoretically, that could help the stock photos website rank in Google for keywords related to stock photography.
Average Position – Average position refers to a “statistic that describes how your ad typically ranks against other ads.” On a search page, Google AdWords has four top positions (1 – 4.) Positions 1 – 4 appear at the top of the search results pages. Ad positions 5+ are displayed at the bottom of the search results page. Google determines ad position by ad rank. Google scores on the marketer’s bid and keyword, ad, and website or landing page quality. The better the score, the better the ranking position for the ad. Ads can vary from position to position throughout the day depending on high bids for the date and time. Google AdWords Tools allow marketers to analyze their ad’s average position.
Audience – The target demographic to focus your ads to attempt to convert. The audience can vary depending on marketing channel, content, product, service, etc. It is also common for an advertiser to have multiple audiences.
Audit – A full scope look at how a website is performing. Often for SEO purposes, this gives the company in-depth look at all aspects of their website, and tells them where they can improve for a more optimized website.
Automation – Using computer programs to perform tasks that are repetitive, that would normally be completed by a human. Email programs can use automation to send email messages to people based on certain triggers (new customers, did or did not open the last email, etc). Marketers also use automation to nurture leads by sending relevant content to previous visitors of a website, in an attempt to get the visitor back to convert into a sale.
B
B2C Digital Marketing – What is B2C Digital Marketing? It’s the practice of advertising products and services to consumers, also called “consumer-to-business.” There are many ways marketers use this strategy such as content marketing or banner ads. One way businesses reach their target audience online through blogs!
B2B Digital Marketing – B2B digital marketing refers to digital technologies and strategies use to reach leads and convert customers. B2B is abbreviated for “Business 2 business.” B2B digital marketing methods allow marketers to focus on targeted, measurable, and interactive audiences. Products and services are promoted through different digital marketing methods like digital content marketing and social media marketing. This type of marketing is considered effective in building brand awareness, preference, and engage with prospects and customers. B2B digital marketing methods include search engine optimization, search engine marketing, influencer marketing, content marketing, e-commerce marketing, data-driven marketing, campaign marketing, content automation, social media marketing, direct email marketing, social media optimization, eBooks, display advertising and optical disks and games.
Backlink – This is when one website hyperlinks to another website using html href code. Backlinks are a major factor used by Google in determining organic rankings. The basic idea being that if “website A” has incoming backlinks from other strong/relevant websites (websites B, C, and D), the links are votes of trust for website A. Website A will then gain authority from B, C, and D through those backlinks, which generally results in better rankings and a source of potential referral traffic.
Banner Ad – A popular type of digital image ad that can be placed across various websites. The largest and most popular image ad network is run by Google.
Bid – The price a marketer will pay to show their ad. Used in pay-per-click advertising, this often refers to keyword bidding, and the amount an advertiser will place on a keyword so Google will consider them in their algorithm.
Bing – A web search engine that provides search services for web, video, image and map search products. Bing is owned and operated by Microsoft, and is powers Yahoo! Search. Bing now controls approximately >20% of the search share.
Bing Ads – A platform that provides pay-per-click advertising on both the Bing and Yahoo! search engines. The service allows businesses to create ads, and subsequently serve the ads to consumers who search for keywords that the businesses bid on. This platform also offers targeting options such as location, demographic, and device targeting.
Blog – A website or web page that consists of personal or informational posts, often in chronological order, to reach an audience interested in that subject. Digital marketers often use or recommend blog posts or pages to improve a company’s content strategy, putting more information about that industry out to the web.
Bots – Also referred to as a ‘Googlebot’ or ‘Spider,’ a bot is a web crawler that discovers new or updated web pages or websites. When a user enters a search query to a search engine, Google’s bot will crawl the internet to find the most relevant results for the user’s search.
Bounce Rate – A term used to describe the percentage of users who leave after only viewing one page of a website, as opposed to clicking on links or navigating to other pages. This helps determine user interest and can serve as a metric to help businesses decide what aspects of their website to optimize.
Brand Awareness – Brand awareness refers to the extent of consumer awareness (recall and recognition) of a brand and its related products. Brand awareness of a brand and its related products are built through various forms of advertising. Brand awareness is essential in business marketing practices as it measures the ability of consumers to recall a brand. Brand awareness is a primary consideration in consumer behavior, advertising management, brand management, and strategy development. Consumers will not purchase unless they are aware of the product category and awareness of the brand within the category is present.
Brand Loyalty – Brand loyalty refers to the positive consumer attitudes towards a brand and consumer commitment to the brand. Brand loyalty is a faithful relationship between consumer and/or the brand, products, or business, regardless of competitor’s actions or product changes. Consumer brand loyalty is displayed in different ways, including brand product purchases and positive word of mouth advocacy.
Buyer Persona – Buyer persona refers to a semi-fictional character or characters used by marketers to represent different buyer types and scenarios. These characters are created from market research and real data used by existing customers and leads. Personas used to represent real type consumers and customers that might visit the site, purchase a product, use the product, etc., in a similar manner. Marketers can combine personas with market segmentation. Qualitative personas are constructed to represent specific segments. Negative buyer personas can also be created and used to describe consumers and customers that marketers would like to avoid.
C
Campaign – A series of advertising messages that share a theme, and market a product or service. In the context of digital marketing, campaigns can be run through search and display network advertising platforms (i.e. Google, Bing), social media, email, or other online platforms. Campaigns can also refer to a comprehensive digital marketing strategy or project.
Channel – The avenue or outlet an advertiser chooses to use to market to their audience. Common marketing channels can be Google, Email, Social Media, Organic, or Paid.
Click-Through-Rate – A metric showing how often people click on an ad or search result after they see it. It can be calculated by dividing the number of clicks, by the number of impressions (how many times the ad or search result was seen). This ratio can be useful when determining whether the messaging matches what the consumer is searching for, and if it resonates with them. A higher click-through-rate means more engagement, which generally leads to more quality conversions.
Code – In Digital Marketing, the code is a set of programming instructions that make up a website or instruct a web page how to perform. There are many different types of code, for example a site could be built on JavaScript, HTML, or XML.
Contact Form – A section on a website with fillable fields that visitors use to contact the website owner. Most commonly used to collect names, phone numbers, and email addresses of potential customers. Contact forms are fast becoming a preferred method for reaching out to a business.
Content – Any form of online media that can be read, watched, or provides an interactive experience. Content commonly refers to written materials, but also includes images and videos.
Copy or Ad Copy – The text associated with an ad. Copy can also be referred to as the main content on the pages of a website, but when talking about ad copy it is usually in reference to the headlines and description that accompany the ad.
Conversion – The completion of a predefined goal. This is often used to track the number of site visitors that have been “converted” into paying customers, though sales are not always chosen as the metric. Other common goals are newsletter subscriptions and content downloads from the website.
Conversion Rate – The rate at which visitors to a website complete the predefined goal. It is calculated by dividing the number of goal achievements by the total number of visitors. For example, if 100 people visit a website and 10 of them complete the conversion goal (like filling out a contact form) then the conversion rate is 10%.
CPA (Cost Per Acquisition) – A metric in paid advertising platforms that measures how much money is spent in order to acquire a new lead or customer. It can be calculated by dividing the total spend by the number of conversions, for a given period of time. For example, if in a month a PPC account spends $1000 dollars and gets 10 conversions (leads), then the cost per acquisition is $100.
Cookie – A small digital file that is stored on the backend of a user’s computer after they visit a site. This can stay on a computer either permanently or temporarily. Users can clear their cookies, or clear cache, to remove any temporarily stored cookies from their website. Cookies can be used by a business to learn about their customer, how they interact with their website, and remarket back to them based off of their interests.
CPC (Cost Per Click) – The amount of money spent for a click on an ad in a Pay-Per-Click campaign. In the Adwords platform, each keyword will have an estimated click cost, but the prices change in real time as advertisers bid against each other for each keyword. Average CPCs can range from less than $1 dollar for longtail or low-competition keywords, to upwards of $100 per click for competitive terms, primarily in legal, insurance, and water damage restoration industries.
CPM – Stands for “Cost Per Thousand” (M is the roman numeral for 1,000). This is the amount an advertiser pays for 1,000 impressions of their ad. For example, if a publisher charges $10 CPM, and your ad shows 2000 times, you will pay $20 for the campaign ($10 x 1000 impressions) x 2. Measuring ad success with CPM is most common in awareness campaigns, where impressions are more important than conversions or clicks.
Crawler – An automated program that scans websites to determine their content and purpose. The name reflects how the software “crawls” through the code, which is why they are sometimes also referred to as “spiders”. Crawlers are used by Google to find new content and to evaluate the quality of webpages for their index. Webmasters and SEOs can request additional scans through Google Search Console.
CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization) – A branch of digital marketing that aims to improve the conversion rate of web pages, thus making the pages more profitable. Conversion rate optimization combines psychology with marketing and web design in order to influence the behavior of the web page visitor. CRO uses a type of testing called “A/B split testing” to determine which version of a page (version A or version B) is more successful.
CSS – Stands for “Cascading Style Sheets”. CSS is a document of code that tells the website’s HTML how it should appear on screen. CSS is a time saving document for web designers, as they can style batched-sections of HTML code, rather than styling individual lines of code one-at-a-time.
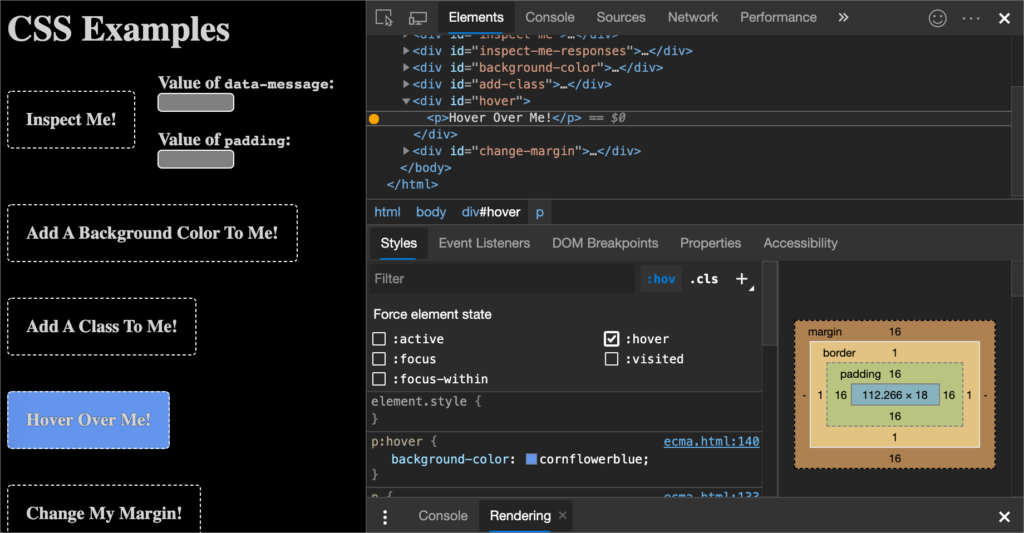
CTA (Call to Action) – An element on a web page used to guide visitors towards a specific action or conversion. A CTA can be a clickable button, an image, or standard text. They typically uses imperative verb phrases like: “call today” or “buy now”.
CTR (Click Through Rate) – the ratio of how many times an advertisement was clicked on, versus how many times it was shown. It is calculated by dividing the ad’s clicks by the ad’s impressions. For example, if an ad is shown to 100 people, and 10 of them click the ad, then it has a click through rate of 10% (10 clicks / 100 impressions = 10%)
Customer Experience – Customer experience refers to the organization and customer relationship quality throughout the consumer/customer and business relationship. The interaction consists of three parts: the customer journey, the customer and business interaction type (over the net, in person, on the telephone, etc.) and the customer environmental experience. A positive customer experience refers to a customer that is satisfied with all points of interaction/experiences with the business.
Creative – The imagery of an advertisement. Creative is the meat of the ad that is meant to draw in the audience’s attention and get them to perform an action.
D
Dashboard – A place to see all important metrics at a glance. Most often used in Google Analytics, this workspace allows an advertiser to track the most important metrics to their business over a designated period of time and determines how users are interacting with their website.
Digital Marketing – A catchall term for online work that includes specialized marketing practices like SEO, PPC, CRO, web design, blogging, content, and any other form of advertising on a internet-connected device with a screen. Traditionally, television was not considered digital marketing, however the shift from cable television to internet streaming means that digital advertising can now be served to online TV viewers.
Digital Marketing Plan – refers to a structured digital marketing promotional plan. The plan is strategic and used to promote brand, products, and services. Digital technologies are used to promote to the marketer’s ideal audience for the best conversion rate.
Directory – A website that categorically lists websites with similar themes. Some directories like chambers of commerce (a list of businesses in one geographic area) can be helpful for SEO, however widespread abuse of spam directories led Google to discount links from directories whose sole purpose was selling links.
Display Ads – A type of online marketing that uses images or video to communicate their ad, rather than text-based advertising. Display advertising is used across platforms like Google AdWords, AdRoll, Facebook, Instagram, and more.
DNS – Stands for Domain Name System, it is a protocol that translates website URLs (which use alphabetic characters) into IP addresses (that use numeric characters). DNS exists because it is more useful for internet users to remember letters and words in website URLs, but the world wide web communicates in numbers with IP addresses. Without DNS, every website would just be a string of numbers rather than a traditional URL.
Dofollow – A phrase that denotes a hyperlink absent of a “nofollow” tag. By default, a hyperlink is a dofollow link until a “nofollow” piece of code is added to it. Dofollow links pass SEO equity to the destination URL, while “nofollow” links do not.
Domain – A name used in URLs to identify web pages and where they belong. For example, in the URL www.alfatek.digital/about, the domain name is alfatek.digital.
Domain Authority – The measure of power a domain name has, and how it ranks in a search engine. The domain authority is based off of three main factors: age, popularity, and size.
Drupal – Drupal is a free and open-source web content management system written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License. Drupal provides an open-source back-end framework for at least 14% of the top 10,000 websites worldwide – ranging from personal blogs to corporate, political, and government sites.
E
E-Commerce – Refers to Electronic Commerce. The term classifies online businesses. A common E-Commerce business is an online retailer that sells products directly to consumers. Computer networks are used to trade or facilitate trading in products or services.
Email Automation – Email automation refers to a marketing system that uses software to send emails automatically. The system uses defined triggers like consumer purchases and email submissions to send emails. Multiple automated emails can be created for use in a sequence. For instance, when a customer purchases a good. The marketer can send a “Thank you” email and keep the customer’s retention with sending Email automation saves marketers time and aids in the marketing funnel.
Email Marketing – A type of content marketing specifically sent through email. Email marketing can be used to distribute content, sales promotions, services, or used to develop relationships with potential customers.
Email List – A collection of email addresses that can be used to send targeted email marketing campaigns. Lists are typically segmented by user classification, so a list of existing customers can receive one type of communication, while potential customers can receive more promotional communication.
Engagement Rate – Engagement rate refers to the percentage of followers or viewers that engage with a post. In other words, engagement rate shows marketers/publishers how much people interact with their published piece. Various factors influence engagement such as users’ comments, share, likes, etc. Engagement rate is a metric strongly used in analyzing social media.
F
Facebook Advertising – Facebook allows advertisers to reach its users through their ad network. A range of ad types can be created to reach various goals set by companies. Facebook advertising is unique in that audiences are set up based on vast demographic information that Facebook has about their users, as compared to Google advertising that uses keywords.
Facebook Profile – A personal Facebook account. Profiles are automatically created when a user signs up.
Facebook Business Page – A public webpage on Facebook created to represent a company. Using a business page gives users access to Facebook Ads Manager. It also allows businesses to engage with users (i.e. page likes, message responses, post content).
Frequency – The number of times an ad makes an impression on one person. Often, advertisers will limit the frequency of an ad so a user doesn’t experience ad fatigue by seeing the same ad too many times, and develop a negative connotation with that advertiser.
G
Google AdWords – Google’s pay-per-click (PPC) advertising platform. AdWords allows you to build, manage, and optimize campaigns, ad groups, ads, and keywords within a single account.
GA or Google Analytics – A platform in Google that tracks and measures various metrics of a website to show an advertiser or company how a user interacts with their website, and how their website is performing as a whole.
GTM or Google Tag Manager – A platform in Google that manages all tags for a website in one place, allowing the advertiser to easily change, update, or add new tags or code snippets to their site without having to go into the backend of the website.
GSC or Google Search Console – Previously named Google Webmaster Tools, it is a service for webmasters to monitor, maintain, and optimize their web presence. Common areas of focus in GSC are site indexing, site traffic, and crawl errors.
Google My Business – The platform on which businesses can input information to appear in the search results, map packs, location searches, and more. Name, address, phone number, website link, hours of operation, reviews and more can all be managed through this tool. GMB is crucial to local SEO campaigns, and is directly related to location-based searches.
Google Algorithm – Google algorithm refers to a mathematical system that is designed for Google search engines to determine where websites will be positioned in the search result pages. The algorithm is also referred to as the “Core” algorithm. Google updates the algorithm approximately 500 to 600 times per year or two times per day. With the update, website positions can fluctuate from day to day. Google’s actual algorithm is kept a secret so that webmasters and marketers cannot manipulate the system to gain higher rankings. Google does provide webmasters and marketers with guidelines on how to appear higher in the search result pages.
H
Hashtag – Hashtag refers to the symbol “#” that is used in social media. Hashtags are used for social media users to find content easily. Hashtags are used for broad topics, detailed topics, and niches.
Header – Can refer to either the top portion of a webpage that typically contains the logo and menu, or the section of HTML in a website’s code that contains important information about the site.
Header Code – On a website, certain code is placed in the universal header section so that it can be accessible across all pages of the website. Typically in the header code, you’ll find things like Schema Markup, Analytics Code, Adwords Code, and other tools used for tracking data across a website. These are placed in the header code so that they can be rendered and start tracking information as the site loads.
Header Tags (h1, h2, h3, etc) – Commonly referred to as the Header tag, or <h1> tag in HTML, it is the title of a page, and will stand out among the rest of the text on a page. Other header tags in HTML include h2, h3, h4 and so on. This represents the hierarchy of titles and subtitles on a page. Google uses these tags when they crawl the backend of a site to get an idea of what that page is about.
Heatmap – A heatmap is a graphical representation of how users interact with your site. Heatmapping software is used to track where users click on a page, how they scroll, and what they hover over. Heatmaps are used to collect user behavior data to assist in designing and optimizing a website.
HTML – A coding language used to create a website. The letters, symbols, and numbers within a text file will determine what a website looks like and how it will perform.
HTTP – Stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. HTTP is the protocol used by the world wide web to define how data is formatted and transmitted, and what actions web browsers and web servers should take to respond to a command. When you enter a website into your web browser and press enter, this sends an HTTP command to a web server, which tells the server to fetch and send the data for that website to your browser.
HTTPS – Stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Is a secured version of HTTP, which is used to define how data is formatted and transmitted across the web. HTTPS has an advantage over HTTP in that the data sent when fetching a webpage is encrypted, adding a layer of security so that third parties can’t gather data about the webpage when the data is sent from the server to the browser.
Hyperlink – A hyperlink is an HTML code that creates a link from one webpage to another web page, characterized often by a highlighted word or image that takes you to the destined location when you click on that highlighted item.
I
Impressions – The number of times an ad is seen by a potential customer. This can be through a search engine results page or through display advertising, and a user does not need to interact with the ad for it to be considered an impression. This is a common metric tracked in pay-per-click campaigns.
Iframe – An HTML document that is inside of another HTML document on a website. Iframes are used commonly to embed content from one source onto another web page.
Inbound Marketing – Inbound marketing refers to the activities and strategies used for attracting potential users or customers to a website. “Inbound” is a more recent euphemism for what has traditionally been called “SEO”. Inbound marketing is crucial to having a good web presence, as it’s used as a way to attract prospective customers by educating and building trust about your services, product and/or brand. (See also: organic)
Inbound Link: Similar to a ‘backlink,’ it is a link directing users to a website from a separate or third-party site. Having a high number of inbound links is very beneficial towards a website’s SEO and domain authority because it is essentially boosting — or endorsing — that website.
Index – The process of gathering and recording all pages on a particular website. This is a commonly-used feature of Google Search Console, where Google will crawl a website to index all current pages, add any new or updated pages, and remove any deleted pages.
Instagram Ads – Instagram Advertising refers to paid advertising on the Instagram platform. The advertising is a paid advertising, meaning advertisers pay to have their ads displayed. Marketers can reach more significant and more targeted audiences. With Instagram advertising, marketers use images or videos with context for advertising.
J
JavaScript – A programming language primarily used in web production that presents itself as animation or movement. Employing JavaScript on a website or page is what makes certain parts interactive, such as the search bar, a video, or a live-feed.
Joomla – Joomla, also spelled Joomla! and sometimes abbreviated as J!, is a free and open-source content management system for publishing web content on websites. Web content applications include discussion forums, photo galleries, e-Commerce and user communities and numerous other web-based applications.
K
Keyword – In Search Engine Optimization, it is a word or set of words that help make up a site’s metadata and describes what is on a web page. When used correctly, a keyword should help users find a web page based on their search terms.
Keyword Phrase – A group of two or more words that are used to find information in a search engine. Sometimes, when searching for something, one single keyword does not provide the information you seek, where a keyword phrase allows you to string multiple words together to find better information.
Keyword Research – Keyword density refers to the percentage of how often a keyword appears on a webpage in relation to the total words on that webpage.
Keyword Stuffing – The practice of researching what terms or phrases people frequently search for and using that data to make informed decisions regarding which keywords a business should be targeting in their own campaign. If done well, keyword research can help businesses rank higher for their targeted terms.
KPI or Key Performance Indicator – A measurable value determined by a company to indicate how well an account is performing and used to evaluate success.
L
Landing Page – A solo web page with a focused sales pitch that is designed to get a visitor to take an action. In a PPC ad, the landing page is the URL destination a user lands on when they click the ad. Different versions of landing pages are often tested against each other in ad campaigns so account managers can see which page performs better.
Lead – A potential customer in the sales funnel who has communicated with a business with intent to purchase through a call, email, or online form fill.
Link – Also known as a hyperlink, a link is a string of hypertext transfer protocol structured text used to connect web pages on the internet. There are two main forms of links: internal links that point to pages on the same site, and external links that point to web pages on a different website.
Local SEO – Local SEO refers to local search engine optimization. Local search engine optimization is similar to search engine optimization as it is to create visibility website or webpage visibility in the organic search engine results pages. Marketers use local SEO to market their business locally. In other words, local SEO is used to help businesses promote their products and services to local customers.
Linkedin Advertising – LinkedIn’s advertising platform. Through different ad formats, advertisers can bid on ad space and target unique audiences based on job title, years of experience, industry, and many other demographics.
M
Marketing Automation – A software or tool that helps automate marketing processes or actions. Oftentimes, it is used for email marketing, social media, or other tasks that require repetition. Examples of marketing automation software include HubSpot, MailChimp and ActiveCampaign.
Metadata – Often in the form of tags, it encompasses the descriptions or keywords used to describe a web page’s content. The two most basic forms of metadata are meta description and meta title, however this can also include the author, when it was created, any open graph tags, and how long the document is.
Meta Description – A tag in the HTML of a web page consisting of key words and phrases that gives a short summary on what the page is about. When properly optimized for SEO, search engines will scan this part of the site to see if that page is relevant to a user’s search. This tag is also kept to a limit of ~160 characters.
Meta Title – Similar to the meta description, this is also a tag in the HTML of a web page that acts as the page title. When properly optimized for SEO, search engines will read this tag first and will continue with the description to determine if the page is relevant. Also referred to as a title tag, this is kept to a 50–60 character limit.
Meta Keywords – A specific meta tag that displays the specific keywords addresses in a page. After meta keyword markup was abused on some websites, listed keywords no longer apply to how a page is categorized by google and other search engines.
Mobile Page Optimization – Mobile page optimization refers to mobile SEO best practices to ensure a website is designed to account for various screen sizes and load times. In other words, it is an optimization that provides a full view of a website on any size screen.
Magento Commerce – Magento is an open-source e-commerce platform written in PHP. It uses multiple other PHP frameworks such as Laminas and Symfony. Magento source code is distributed under Open Software License v3.0.
N
NoFollow – A value that can be assigned to a rel attribute to tell a search engine that the outbound hyperlink should not influence the link target’s ranking in a search engine index. It allows one site to link to another without influencing that site to rank better.
Niche Marketing – Niche marketing refers to a concentrated type of marketing. It is strategic marketing that is used to target distinct audiences. The idea of niche marketing is to target smaller segments of the online population for more significant marketing results. Marketers identify the needs, wants, and requirements of a group of consumers to target the consumers strategically.
O
Organic Traffic – Users coming to a website on their own through a search engine, like Google or Bing. Unlike paid traffic, these users are coming to a website unprompted and uninfluenced by advertisements. This is a common metric that business owners strive to increase.
Outbound Link – A link that comes from your website that allows the customer to leave your website and move to another domain. These are often paired with a NoFollow that removes the Inbound link for the other website (See: NoFollow).
Organic – A source of traffic to a website that comes through clicking on a non-paid search engine result. Organic traffic is a primary measurement of an SEO campaign and will generally grow as a site ranks better for relevant keywords in search engines.
On Page SEO – refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in the search engines. Ranking higher most often equivalates to generating more traffic. Keyword and phrase base for more relevant traffic. On page SEO is referring to the content and HTML source code of a page that marketers can optimize for better search ranking and results.
P
Page Speed – The time it takes for the content on a web page to load on a browser or mobile device. While this is highly important for user experience, this is also becoming an increasingly important part of SEO optimization; the slower a page loads, the fewer pages search engines can crawl within their allocated crawl time. From a user experience standpoint, the slower a page loads, the higher the bounce rate will tend to be.
Paid Search Traffic – The number of users that come to a web page through a paid advertisement, typically through a PPC channel such as Google AdWords or Facebook Advertising.
PPC or Pay-Per-Click Advertising – A form of online advertising in which advertisers only pay for their ads when a user clicks on them. Common PPC channels are AdWords, Bing, and Facebook.
Position – The placement in a search engine’s (Google, Bing, etc) search results, where a site ranks for a specific query or keyword.
Penalty – An infraction issued by Google, to a webmaster, for breaking Google’s guidelines. The penalty is issued by Google through Search Console, and can result in a sites’ removal from search engine results. The issues that caused the penalty will need to be fixed before the penalty is lifted, and once the penalty is lifted it may still take some time to return to previous rank in Google search results.
Pinterest Ads – Pinterest advertising refers to Pinterest social media ad service. The social media platform provides marketers with the option pay to displays ads. Pinterest ads look like regular Pins only they are displayed to a broaden Pinterest audience. Pinterest users, also called Pinners, can save pins to various boards to revisit later. When the pin is a promoted pin, the user’s followers will also see the ad in their feeds.

Pixel – A piece of code used to track a goal that lives in the backend of a website. Different platforms have various pixels that all service different purposes. Pixels can track conversions or form fills, count purchase orders and revenue from users that come through an ad, and they can even tag a user’s computer by placing a cookie on their browser that allows the company to remarket their goods and services back to them after the user leaves their site.
Q
Quality Score – Google Adwords’ rating of the relevance and quality of keywords used in PPC campaigns. These scores are largely determined by relevance of ad copy, expected click-through rate, as well as the landing page quality and relevance. Quality score is a component in determining ad auctions, so having a high score can lead to higher ad rankings at lower costs.
Query – The term given for what a user types and searches using search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. Examples of queries include “austin electrician,” “how do i know if i have a raccoon in my attic,” “distance to nearest coffee shop,” and many more.
R
Rankings – A general term for where a website appears in search engine results. A site’s “ranking” may increase or decrease over time for different search terms, or queries. Ranking is specific to each keyword, so a website may have keywords that rank on the first page, and others that don’t.
Referral – A medium denoted in Google Analytics that represents a website visit that came from another website (as opposed to coming from a Google search, for example). When users click on a link to another, external webpage, they are said to have been “referred” there.
Remarketing – remarketing is Google AdWords’ solution that is specific to their network. However, remarketing is confined to email and phone. For example, if a person browses a shopping website and abandons their cart, a remarketing email may be sent to that person to remind them of their almost-purchase.
Retargeting – when ads for a business’ product or service are shown across the web to people who have visited their website previously. Retargeting reintroduces the product or service to those who are more likely to buy, because they have already shown interest in the past. When a person browses a website, a cookie tracks them anonymously, and shows them targeted ads based on their browsing behavior.
RLSA or Remarketing Lists for Search Ads – A Google AdWords function that allows businesses to create lists based on customer behavior from their website visit. Depending on the parameters set, businesses can add tags to certain pages of their website, adding customers who visit those pages to a list. Google will then attach cookies, so when the customer searches for similar items, you can bid more for keywords, or target ads to the customer directly.
ROAS or Return on Ad Spend – Refers to the value, monetary or otherwise, a business will receive from the money they put into advertising.
Robots.txt – A text file stored on a website’s server that includes basic rules for indexing robots which “crawl” the site. This file allows you to specifically allow (or disallow) certain files and folders from being viewed by crawler bots, which can keep your indexed pages limited to only the pages you wish.
ROI or Return on Investment – The benefit received from a certain investment compared to the cost. In technical terms, the formula is (gain-cost) divided by the cost, but can be based on a number of metrics. For example, a business’ ROI in digital marketing could take into account the cost of the investment in addition to leads and conversions as part of the equation.
Responsive Web Design – Responsive web design refers to a website creation that adjusts page content to the screen size or device to be displayed accurately. In other words, a complete and correct visual display of the page content is accurately shown regardless of the screen size of the device. With responsive web design, a website “responds” to the screen size of the user’s device and will adjust the site’s content and images to fit the screen perfectly.
S
Search Network – A group of websites in which ads can appear. Google’s Search Network, for example, is a group of Google & non-Google websites that partner with Google to show text ads.
Search Engine – a program that searches an index of information and returns results to the user based on corresponding keywords. The most well known search engines are Google, Youtube, Bing, and Yahoo.
SEM or Search Engine Marketing – A form of PPC marketing that targets users’ search engine results in the form of relevant ads and results.
SEO or Search Engine Optimization – Incorporating factors such as keywords, good copy, and backlinks in order to drive traffic and affect the visibility of a site organically. This is done by optimizing the content of a web page and increasing its relevance to certain keywords. By doing so, the website is more likely to show when a user searches for the targeted keywords.
SERP or Search Engine Results Page – The resulting list a user receives after typing in a search query in a search engine. It may be a mix of ads and organic search results.
Sessions – The duration of time a user spends on a particular web page. It is a useful metric for determining engagement and may require better content and a friendly user interface to increase average session duration.
Sitemap: A structured list of the pages within a website that helps search engines index the site. Having a sitemap helps users find and navigate the site based on their query.
Slug – Slang for the portion of a URL that comes after the .com. For example, the homepage might be http://www.alfatek.digital, but for the Contact Us page, a slug would be added to the end of the URL to direct the browser to a page within the website i.e. http://www.alfatek.digital/about.
SSL Certificate – These small data files are added to web servers that then allow a website to use the HTTPS protocol. SSL certificates digitally connect a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. Originally, these were used to secure logins, data transfers and credit card transactions, but have recently become the go-to system for websites, especially after the Google Chrome update that displays a warning message to users, if the certificate is not present.
Social Media Traffic – Social media traffic refers to a website, mobile site, or mobile app traffic from social media sites. In other words, the visitor is directed to the site from a social media platform. Social media platforms include Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and Pinterest. When an ad or link is clicked from a social media site, the user is directed to the site, and their visit is considered social media traffic. Social media traffic can result from paid or organic advertising.
T
Target Audience – Target audience refers to a specific group of people with shared characteristics that meet a marketer’s buyer personas. In other words, they are the audience that is likely to be the most interested in a marketer’s product or service and to purchase. Typically, a target audience is defined through demographic information.
Tag – In WordPress, a tag is an identifying marker used to classify different posts based on keywords and topic. Similar to WordPress categories, but tags are more granular and specific, whereas categories are broad and thematic.
Title Tag – An HTML element that is used to describe the specific topic of a web page. Title tags are displayed in the tabbed top bar of a web browser. In SEO, it is best practice to have descriptive title tags featuring your main keywords, rather than something basic like “home”.
Twitter Ads – Allows marketers to promote a tweet on users feeds without that user having to follow your brand for it to appear on their feed. These advertisements can be used to grow brand awareness, gain more followers, extend social media reach, and/or reach out to prospective customers about a product or service.

U
URL – stands for Uniform Resource Locator and is the address of a web page. The URL refers to what specific web page a web browser is viewing.
Unique Visitors -A metric used in web analytics to show how many different, unique people view a website over a period of time. Unique visitors are tracked by their IP addresses. If a visitor visits the same website multiple times, they will only be counted once in the unique visitors metric.
User Interface (UI) – refers to the abbreviation for a user interface. User interface refers to the means by which a user and digital device interact. For example, input devices and software use and a site’s visitor behavior while on the site. A user interface should be user-friendly.
User Experience (UX) – refers to the abbreviation for User Experience. UX refers to the manner a user interacts with a website or app. For instance, the web pages a visitor visits while on a site, how the visitor scrolls a page, and areas the visitor “hovers” over on a page, etc. Knowing visitor site behavior, or UX helps marketers to improve conversion rates. It is essential for marketers to have a good UX for the sake of business as a good UX drives repeating users and engagement.
V
Value Proposition – A statement promising a service, good, or feature that a customer would benefit from when purchasing a product or service.
Visitors – A metric in Google Analytics that quantifies a user of a website over a particular period of time. Visitors are often broken down between “new visitors” who are browsing for the first time in the allotted time period, or “returning visitors” who have already browsed at least once in the given time frame.
W
Web page – A single page that lives on a domain within a website on the World Wide Web. They are a document written using HTML and display data that can usually be accessed by anyone.
Website – An address on the Internet made up of a collection of web pages that are connected to one another in order to host information and data.
Website Analytics – Website analytics refers to the analysis and reporting of web data to better understand website visitor behavior. Specific data is measured and analyzed for an informed understanding of user behavior across web pages. Various data includes the amount of time a visitor spends on a page, how many pages of a website site visitors visit while on the site, how long they stay on the site, and how they arrive at the site are all measured and analyzed for website analytics.
WordPress – A free and open-source content management system that allows businesses to integrate plugins, themes, and other services with an pre existing website. Businesses often use it for its content management and creation ability.
Wireframe – Wireframe refers to a cursory layout drawing that acts as a “draft” of a web page in the design process. The draft or sketch focuses on interactive functionality and the rough layout to quickly build the design/page. Wireframing requires experience and expertise in the web design field.
X
XML – Stands for eXtensible Markup Language. Similar to HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) in that it is primarily used to categorize various data for computers and humans to use more effectively. In basic terms, XML allows for customizable tags for marking up information that is otherwise difficult for computers to understand.
XML Sitemap – A document in XML format that categorizes all relevant pages, posts, files, etc. of a website. This document is not intended for human use, though it can be viewed by humans. Instead, an XML sitemap is designed to help search engine crawler bots easily find all of the pages for a given website – very similar to a roadmap or atlas that one would use when driving a car long distances.
Y
Yelp – A social review platform and search engine that allows users to leave reviews for businesses. Yelp also offers an advertising program which gives advertisers the ability show their marketing assets to qualified Yelp users based on keyword searches.
Yoast – A web-optimization company, they offer advanced WordPress plugins and services to help the functionality of user websites. This includes keyword and SEO analysis, Google integrations, and XML sitemap integrations.
YouTube ads – YouTube offers advertising in 6 different formats. Display ads, overlay ads, skippable video, non-skippable video ads, bumper ads, and sponsored cards. These ads can all be created and run through the Google Adwords platform.
Yahoo! Search – One of the largest search engines in the world. As of 2009, the platform has been powered by Bing.
Yahoo! Advertising – Yahoo and Bing ads are both run through the Bing Ads platform. These search engines share advertising networks.




